Arithmetic Operators
C provides all the operators for a basic arithmetic operation. They are listed in the table;
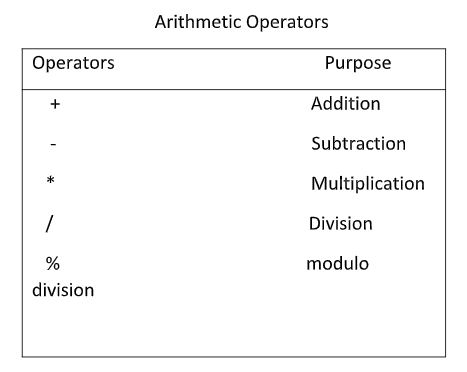
The data items that operators act upon are called operands. Operands acted upon by arithmetic operators must be integer, floating – point or character. Modulo division operator (%) requires both the operands should be integer. Both division operator (/) and modulo division operator (%) require that the second operand should be nonzero. If both the operands of division operator are integer than the result will be a truncated quotient, is referred to as integer division. For example:
a + b
a – b
a * b
a / b
a % b
In the above example, a and b are variable and are known as operands. Note that, there is no exponentiation operator in C.
Integer Arithmetic:
An arithmetic operation involving only integer operands is called integer arithmetic. In the example given below both a and b integer variables. Let a = 17 and b = 5
a + b = 22
a – b = 12
a * b = 85
a / b = 3 (decimal part is truncated)
a % b = 2 (it gives remainder of division)
During modulo division, the sign of the results is always the sign of the first operand (I.e. the dividend). Hence,
-17 % 5 = -2
-17 % -3 = -2
-17 % -3 = 2
Real Arithmetic:
An arithmetic operation involving only real operands is called real arithmetic. In the example given below p, q, and r are floating – point variables.
p = 2. 0 / 3. 0 = 0. 666667
q = 3. 0 / 4. 0 = 0.750000
r = -6. 0 / 7. 0 = -0.857143
The operator % cannot be used with real operands.
Mixed – mode Arithmetic:
When one of the operands is real and the other operand is integer, the expression is called maxed mode arithmetic expression. Thus
17/10.0 = 1.7
About the Author
Silan Software is one of the India's leading provider of offline & online training for Java, Python, AI (Machine Learning, Deep Learning), Data Science, Software Development & many more emerging Technologies.
We provide Academic Training || Industrial Training || Corporate Training || Internship || Java || Python || AI using Python || Data Science etc


